 Some dusty parts of Mars get as cold at night year-round as the planet’s poles do in winter, even regions near the equator in summer, according to new NASA findings based on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter observations. [The findings are reported in the Journal of Geophysical Research.]
Some dusty parts of Mars get as cold at night year-round as the planet’s poles do in winter, even regions near the equator in summer, according to new NASA findings based on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter observations. [The findings are reported in the Journal of Geophysical Research.]
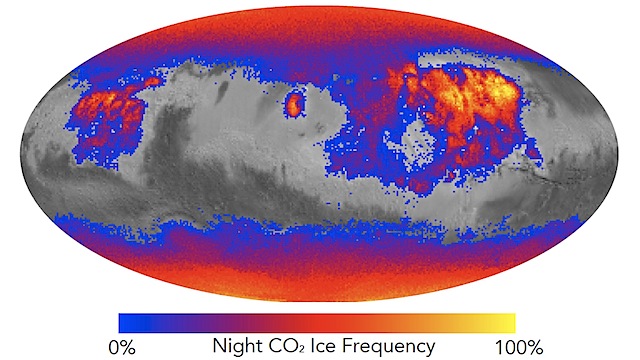
The surface in these regions becomes so frigid overnight that an extremely thin layer of carbon dioxide frost appears to form. The frost then vaporizes in the morning. Enough dust covers these regions that their heat-holding capacity is low and so the daily temperature swing is large. Daily volatilization of frost crystals that form among the dust grains may help keep the dust fluffy and so sustain this deep overnight chill. (…)
Here’s what’s new knowledge: the presence and extent of transient overnight carbon dioxide frosts, even at middle and low latitudes. Infrared-wavelength observations of dust-covered regions by the Mars Climate Sounder instrument on NASA’s Mars Reconnaisance Orbiter not only indicate cold-enough nighttime surface temperatures for carbon dioxide frost to form, they also detect a spectrum signature at night consistent with a trace of frost.
“The temperature gets so low, you start freezing the atmosphere onto the surface,” said Sylvain Piqueux of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, lead author of a report on these findings published online by the Journal of Geophysical Research. “Once you reach that temperature, you don’t get colder, you just accumulate more frost. So even on the polar caps, the surface temperature isn’t any colder than what these lower-latitude regions get to overnight.” [More at links]








