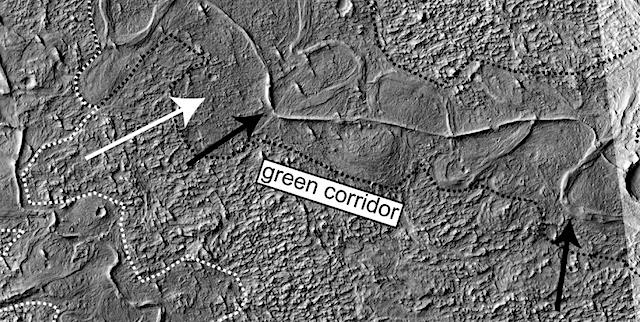
 River deposits exist across the surface of Mars and record a surface environment from over 3.5 billion years ago that was able to support liquid water at the surface. A region of Mars named Aeolis Dorsa contains some of the most spectacular and densely packed river deposits seen on Mars. These deposits are observable with satellite images because they have undergone a process called “topographic inversion.” where the deposits filling once topographically low river channels have been exhumed in such a way that they now exist as ridges at the surface of the planet.
River deposits exist across the surface of Mars and record a surface environment from over 3.5 billion years ago that was able to support liquid water at the surface. A region of Mars named Aeolis Dorsa contains some of the most spectacular and densely packed river deposits seen on Mars. These deposits are observable with satellite images because they have undergone a process called “topographic inversion.” where the deposits filling once topographically low river channels have been exhumed in such a way that they now exist as ridges at the surface of the planet.
With the use of high-resolution images and topographic data from cameras on orbiting satellites, B.T. Cardenas and colleagues from the Jackson School of Geosciences identify fluvial deposit stacking patterns and changes in sedimentation styles controlled by a migratory coastline. They also develop a method to measure river paleo-transport direction for a subset of these ridges. [Their work was published in the GSA Bulletin.] (…)
Cardenas and colleagues conclude that similar falling and rising water levels in a large water body forced the formation of the paleo-valleys in their study area. Cross-cutting relationships are observed at the valley-scale, indicating multiple episodes of water level fall and rise, each well over 50 meters, a similar scale to eustatic sea level changes on Earth. [More at links]








