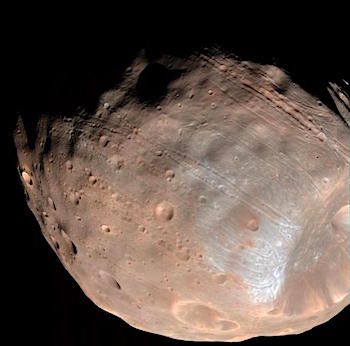
 A new study bolsters the idea that strange grooves crisscrossing the surface of the Martian moon Phobos were made by rolling boulders blasted free from an ancient asteroid impact.
A new study bolsters the idea that strange grooves crisscrossing the surface of the Martian moon Phobos were made by rolling boulders blasted free from an ancient asteroid impact.
The research, published in Planetary and Space Science, uses computer models to simulate the movement of debris from Stickney crater, a huge gash on one end of Phobos’ oblong body. The models show that boulders rolling across the surface in the aftermath of the Stickney impact could have created the puzzling patterns of grooves seen on Phobos today.
“These grooves are a distinctive feature of Phobos, and how they formed has been debated by planetary scientists for 40 years,” said Ken Ramsley, a planetary science researcher at Brown University who led the work. “We think this study is another step toward zeroing in on an explanation.” [More at links]








