NASA’s Opportunity Mars rover will drive down a gully carved long ago by a fluid that might have been water, according to the latest plans for the 12-year-old mission. No Mars rover has done that before.
NASA’s Opportunity Mars rover will drive down a gully carved long ago by a fluid that might have been water, according to the latest plans for the 12-year-old mission. No Mars rover has done that before.
The longest-active rover on Mars also will, for the first time, visit the interior of the crater it has worked beside for the last five years. These activities are part of a two-year extended mission that began Oct. 1, the newest in a series of extensions going back to the end of Opportunity’s prime mission in April 2004. (…)
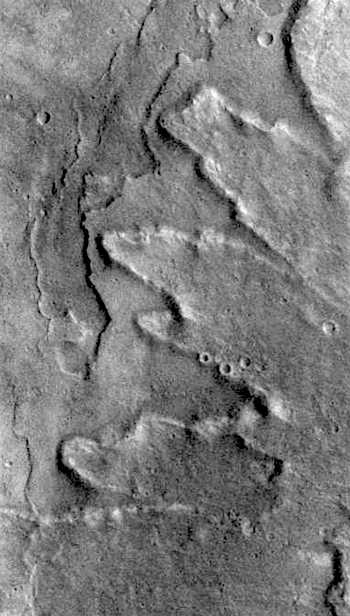
Opportunity begins its latest extended mission in the “Bitterroot Valley” portion of the western rim of Endeavour Crater, a basin 14 miles (22 kilometers) in diameter that was excavated by a meteor impact billions of years ago…. The gully chosen as the next major destination slices west-to-east through the rim about half a mile (less than a kilometer) south of the rover’s current location. It is about as long as two football fields.
“We are confident this is a fluid-carved gully, and that water was involved,” said Opportunity Principal Investigator Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, New York. “Fluid-carved gullies on Mars have been seen from orbit since the 1970s, but none had been examined up close on the surface before. One of the three main objectives of our new mission extension is to investigate this gully. We hope to learn whether the fluid was a debris flow, with lots of rubble lubricated by water, or a flow with mostly water and less other material.”
The team intends to drive Opportunity down the full length of the gully, onto the crater floor….. [More at link]
 This image shows the edge of the Martian South Polar layered deposit. The stack of fine layering is highlighted by the rays of the polar sun.
This image shows the edge of the Martian South Polar layered deposit. The stack of fine layering is highlighted by the rays of the polar sun.